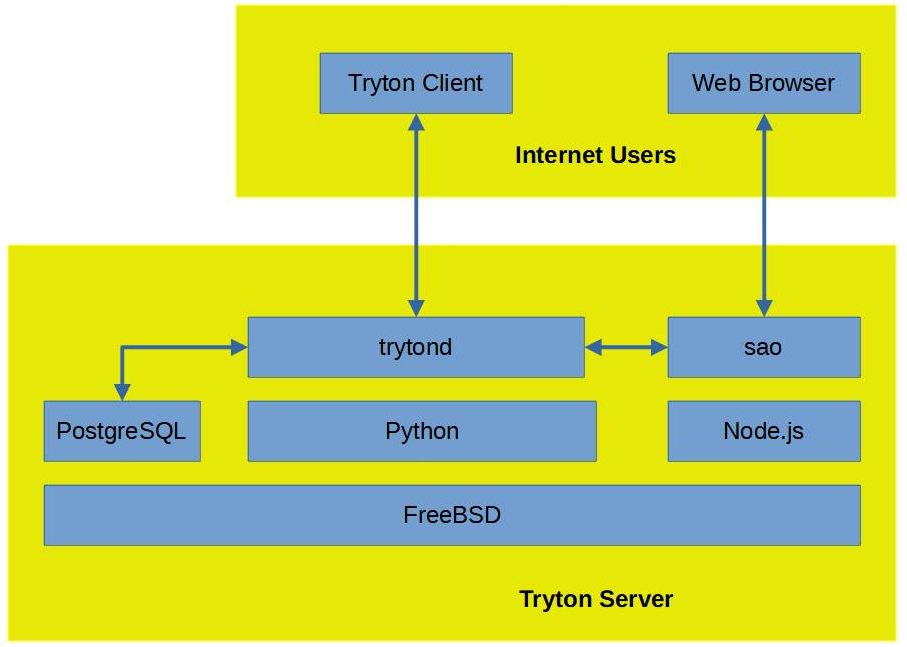
In this tutorial I will install PostgreSQL and configure it as the Tryton data tier. If you have not installed Tryton yet, see Install Tryton on FreeBSD 13.
In Install Tryton on FreeBSD 13, I used SQLite for for basic testing. However, real-world enterprise use with multiple users interacting simultaneously requires high concurrency and ACID compliance for effective and reliable operation. For production, Tryton uses PostgreSQL for its backend or data tier.
Install PostgreSQL
Install the latest version of PostgreSQL (currently 14.1).
% sudo pkg install postgresql14-server
The installation procedure creates a “postgres” user who owns the PostgreSQL files and the postgres server process. The installed configuration file (/var/db/postgres/data14/postgresql.conf) allows access only from the localhost, which will be sufficient since trytond is running locally.
Confirm PostgreSQL installed correctly.
% pg_config --version
Edit /etc/rc.conf to start the server at startup.
% sudo vi /etc/rc.conf ... postgresql_enable="YES"
Initialize a database cluster (one or more databases managed by a single postgresql instance) and start postgresql.
% sudo /usr/local/etc/rc.d/postgresql initdb % sudo service postgresql start % sudo service postgresql status
Use the PostgreSQL createuser command to create a “tryton” PostgreSQL super-user. The “tryton” user will be able to create databases and roles.
% sudo su postgres $ createuser -sdrP tryton Enter password for new role: Enter it again: $ exit %
and restart PostgreSQL.
% sudo service postgresql restart
Confirm that the “tryton” user on localhost can connect to the PostgreSQL server (the “-W” switch causes psql to prompt for the user password).
% psql --username=tryton -W --list
Password:
List of databases
Name | Owner | Encoding | Collate | Ctype | Access privileges
-----------+----------+----------+---------+---------+-----------------------
postgres | postgres | UTF8 | C | C.UTF-8 |
template0 | postgres | UTF8 | C | C.UTF-8 | =c/postgres +
| | | | | postgres=CTc/postgres
template1 | postgres | UTF8 | C | C.UTF-8 | =c/postgres +
| | | | | postgres=CTc/postgres
(3 rows)
%
Install psycopg2
trytond uses psycopg2 to connect to postgresql. Install psycopg2 into the virtual environment created for trytond.
(env) [~/work/trytond]$ pip install psycopg2
Edit trytond.conf to use PostgreSQL
Edit ~/work/trytond/trytond.conf to specify using PostgreSQL backend.
[database] # connect to postgresql using a TCIP/IP port #uri = postgresql://tryton:password@localhost:5432 # connect to postgresql using a Unix socket uri = postgresql://tryton:password@/ [web] listen=0.0.0.0:8000 root = /home/dale/work/sao
Create a Tryton database
I need to use the PostgreSQL createdb command to create a database for Tryton,
% sudo su postgres $ createdb scc
I will use the psql utility to verify the database was created, and then return to my own user name.
$ psql
psql (14.1)
Type "help" for help.
postgres=# \l
List of databases
Name | Owner | Encoding | Collate | Ctype | Access privileges
-----------+----------+----------+---------+---------+-----------------------
postgres | postgres | UTF8 | C | C.UTF-8 |
scc | postgres | UTF8 | C | C.UTF-8 |
template0 | postgres | UTF8 | C | C.UTF-8 | =c/postgres +
| | | | | postgres=CTc/postgres
template1 | postgres | UTF8 | C | C.UTF-8 | =c/postgres +
| | | | | postgres=CTc/postgres
(4 rows)
postgres=# \q
$ ^D
%
Finally I will initialize the database using the Tryton trytond-admin utility.
I will need to activate the virtualenv created for trytond in order to use trytond-admin.
% bash [~/work/trytond]$ source env/bin/activate (env) [dale@starlord ~/work/trytond]$ trytond-admin -c ./trytond.conf -d scc --all -v "admin" email for "scc": dale@dalescott.net "admin" password for "scc": "admin" password confirmation: (env) [~/work/trytond]$
Start trytond
Start trytond specifying the updated configuration file. Notice I will not specify a database as I did when using SQLite. The database will be selected by the Tryton client.
(env) [~/work/trytond]$ env/bin/trytond -c ./trytond.conf
Access Tryton
You can now use the Tryton client to connect to the Tryton server (trytond). A wizard will lead you through the interactive configuration, which will be covered in a seperate post.