(updated January 2024)
Modbus is a communication protocol for industrial devices developed in 1979 by Modicon, now Schneider Electric.
A Modbus network consists of up to 247 Servers (originally Slave), and typically one Client (originally Master). A server is commonly a dedicated end-point device, such as a sensor or control device, and a client is commonly a Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) or gateway device in a SCADA network. A client reads or writes to the Coils and Registers in a server, whose purpose is unique to that server.
A Modbus communication starts when a client sends a message to a specific server, either requesting current coil states or register values, or sending states or values for the server to use. The server responds with either the requested data, or confirmation the sent data was accepted.
Modican designed the Modbus protocol for their PLC products, and freely provided the specification so that others could communicate with their PLCs. Modbus has since become a de facto industry standard for industrial devices, due at least in part to the specification being freely available to use. Modbus has evolved over time to remain current, starting with Modbus ASCII using serial RS-232 and RS-485 communications, then binary Modbus RTU for efficiency (also using RS-232 and RS-485), and more recently Modbus TCP for use with Ethernet networks.
The Modbus specification is now controlled by Modbus.org, a U.S. non-profit trade association, which continues to freely publish the Modbus protocol specifications and related technical resources.
Interest in Modbus has surged recently for use in the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT). Modbus TCP enables data to be exchanged over a wide network, leveraging the advantages of Ethernet and the IwIP network stack for wireless end devices.
For testing and evaluation, general purpose Modbus software running on a desktop or laptop computer is often more convenient than using a purpose-designed Modbus device. A Modbus Client (Master) simulator can be used to query data from devices, and can be a valuable test tool when developing a Modbus Server (Slave) device. A Server (Slave) simulator can be useful as a digital twin for verification testing when developing a physical slave device, or as a device to interact with when developing a Modbus Client.
The following is a non-comprehensive list of available Modbus Server and Client software. If one of these doesn’t quite suite your needs, you consider adapting an existing open-source project or create your from-scratch solution using an open-source Modbus library.
Please post a comment to say if you have found any of these useful, or if you use software that is not listed.
Free Client (Master) Simulators
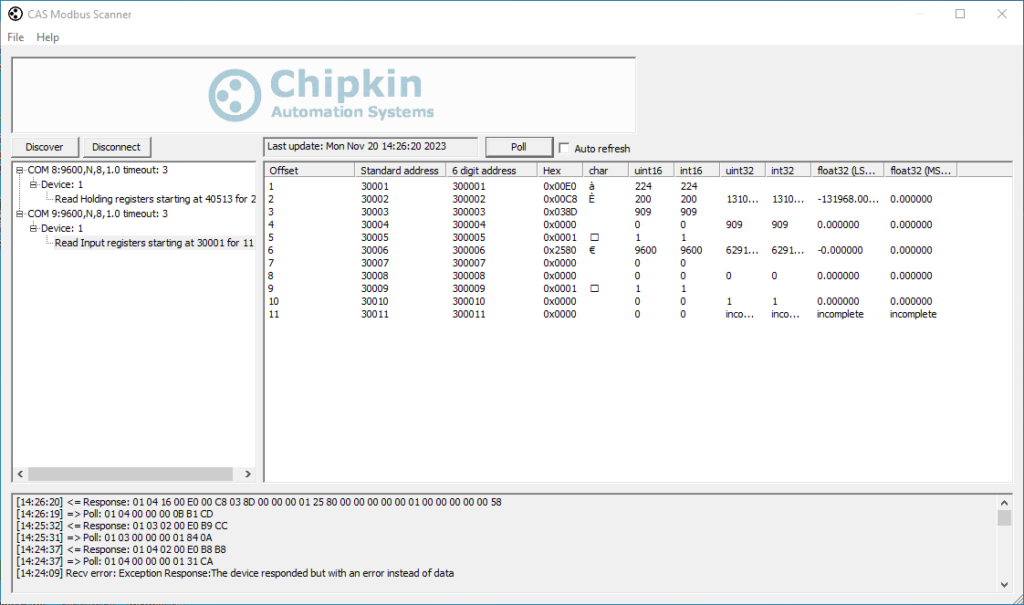
CAS Modbus Scanner
CAS Modbus Scanner is free Windows-only software from Chipkin Automation Systems recommended by Stephen. CAS Modbus Scanner can retrieve coils, inputs, holding registers, and input registers (displaying values in a variety of formats), and also discover Modbus devices on a network (testing every address, function, length, and offset to check for exceptions or responses). Source is not provided.
The scanner function came in handy recently when I used it as part of the verification test program for a new industrial controller.
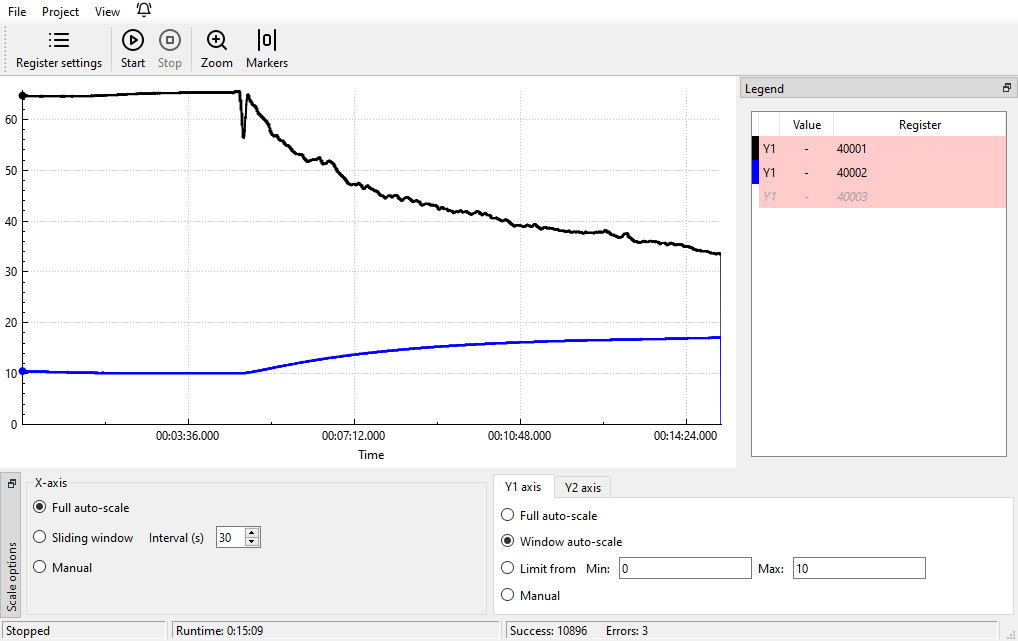
ModbusScope
ModbusScope is a free open-source cross-platform app for capturing and graphing Modbus data. In the past, I would capture Modbus data using Modpoll and hammer the output into CSV with sed, or use ModScan to capture CSV directly, and plot using using either DatPlot or spreadsheet software. However, thanks to Ben’s comment, ModbusScope is now my go-to for data logging and capture when I’m looking at three or fewer registers from up to three devices.
ModbusScope is a Qt app and coded in C++, and uses muparser (“fast math parser library”) and QCustomplot (“easy to use plotting widget for Qt”), with icons from Lucide.
Modbus Tester
Modbus Tester from Schneider Electric is a free proprietary Windows GUI program for reading Modbus registers, and supports Modbus RTU and TCP. I found “Tester” did what it claimed, but it didn’t do anything better than I was already doing with other software.
modpoll
modpoll from proconX is a command-line program for Windows and Linux. It supports Modbus ASCII, RTU and TCP, and is a de facto standard based on the number of references it has on the web.
proconX provides modpoll as reference software for their commercial driver libraries. Source is provided, but compiling requires a paid license for the libraries.
mbpoll
mbpoll is an open source (GPL-3) cross-platform command-line utility based on libmodbus (see Libraries). It supports Modbus RTU and TCP and is available in many (most?) Linux distributions. mbpoll conveniently uses similar output syntax and command options as modpoll, I use mbpoll on a Linux Mint test computer and the two are essentially interchangeable. Unfortunately, although mbpoll claims to be multiplatform, I haven’t found a pre-built Windows binary and have found building from source on Windows to be problematic (if you are building mbpoll on Windows, please submit a comment explaining your procedure).
QModMaster
QModMaster is a free open-source Qt-based Modbus master based on libmodbus (see Libraries below). QModMaster is licensed using the LGPL and includes a bus monitor for examining traffic on the bus.
A binary executable is available for Windows, but using on Linux will require compiling the from source using Qt Creator (which I was unable to do successfully, so on Linux I use ModbusScope or Scanbus-BR when I prefer GUI software).
RMMS
Radzio! Modbus Master Simulator (RMMS) is a free proprietary Windows utility (GUI) and claims to replace commercial ModScan and Modbus Poll utilities. It supports Modbus RTU and TCP, and multiple Modbus slave devices.
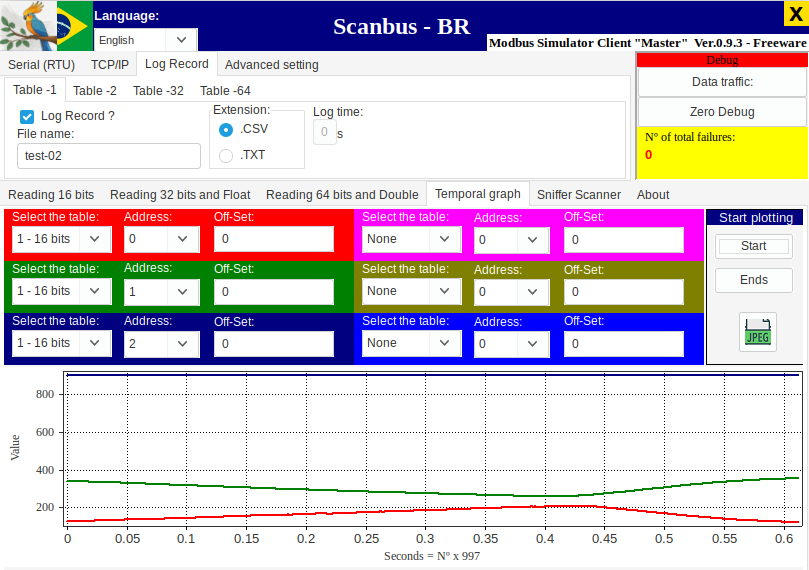
Scanbus-BR
Scanbus-BR is is a free cross-platform multi-lingual Modbus RTU and TCP GUI client (Windows and Linux, and Portuguese, Spanish and English). Rodrigo Hernandes created Scanbus to scratch his own itch and released it publicly to help others and as a demo to support his project development work (he is also a Brazilian, which presumably is the reason for the “- BR” suffix). I found the charting capability very handy (plotting up to six registers vs time), and having register values shown in integer, hex and binary simultaneously saved time by not having to convert or switch display formats.
Paid Client (Master) Simulators
Modbus Poll
Modbus Poll from modbus tools was designed to help developers of Modbus slave devices and others to test and simulate the Modbus protocol. Using a multiple document interface, several Modbus slaves and/or data areas can be monitored at the same time. US$129 per developer. The modbus tools website also has a good intro to Modbus.
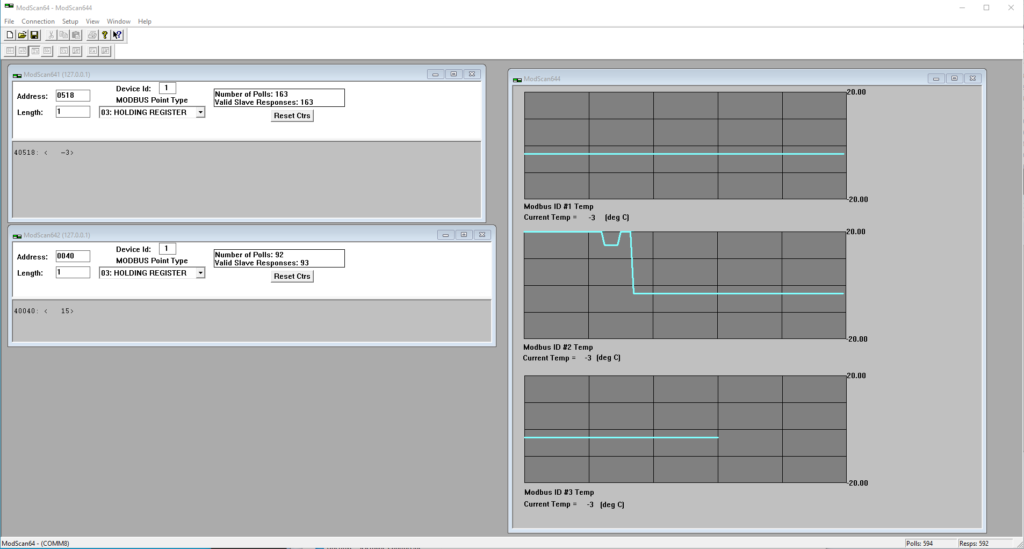
ModScan
ModScan from WinTECH Software was developed to verify correct protocol operation in new or existing systems. ModScan supports an arbitrary number of queries, each with its own document window, and you can create your own custom windows and add content using the provided widgets (for example, using the trendline display shown below, which can plot up to four difference sources in one display). The data from each document window can be logged to its own data file.
Extensions provide third-party data acquisition using Control Automation routines or the MS Jet Database engine, and a debug mode displays raw serial data to and from a connected device. A single-user license cost US$65 when I last checked.
Simply Modbus Master
Simply Modbus Master (RTU and ASCII ). The Free mode allows six request messages before the application must be re-started. C$60. A slave simulator and TCP client are also available. The website has a nice intro to Modbus and Modbus Enron.
Free Server (Slave) Simulators
ModRSsim2
ModRSsim2 was forked from MOD_RSSIM and includes compiling on Visual Studio 2010. ModRSsim2 supports RS-232 and TCP/IP connections, the full range of Modbus addresses for all four Modbus types (0xxxxx, 1xxxx, 3xxxx, & 4xxxx addresses), as well as diagnostics with complete traffic byte capture and logging capability. ModRSsim2 supports CSV loading and a scripting environment for testing as well as HTML custom displays. It is free and open-source, and licensed under the GPL.
MOD_RSSIM
MOD_RSSIM is a Windows-based Modbus PLC Simulator (and parent of ModRSsim2). It is free and open-source, and started as a test program for a SCADA/HMI with Modbus RTU and TCP/IP. Typical uses are to verify device configuration, support development of Modbus master and slave drivers for embedded and desktop platforms, and as an educational tool to learn Modbus protocols.
pyModSlave
pyModSlave is a free and open-source Qt-based Python-code ModBus RTU and TCP slave from the developer of QModMaster. A Windows executable is provided and pyModSlave includes a bus monitor for examining all traffic on the bus. pyModSlave is licensed under the LGPL
UnSlave Modbus Slave Simulator
UnSlave Modbus Slave Simulator . UnSlave simulates any number of Modbus slaves. UnSlave is provided free from Unserver, possibly as a source of test data for Unserver’s Modbus REST API Server, which provides data from Modbus networks and devices to higher-level clients – and is monetized. The informative Complete Modbus Guide is also provided by Unserver.
Paid Server (Slave) Simulators
SimServe
SimServe by SCADAmatic can simulate Modbus ASCII, RTU, or TCP/IP. It provides a user interface for setting up a network topology of multiple devices simultaneously. The developer James brought it to my attention, and was kind enough to provide a guest key for evaluation. SimServe could be a valuable development aid if you are developing SCADA software and need simulated devices for testing, or if you are developing a device and could benefit from having a digital twin for comparison (assuming SimServe is capable of simulating your device).
WinModbus
WinModbus is a Modbus Slave Simulator for Windows. When I found it, the price was GBP62.50 which included lifetime support. A 14-day functional demo is available, and there is an attractive polished website.
Libraries
A number of Modbus libraries are available to leverage application development.
FreeMODBUS
FreeMODBUS is a free open-source implementation of the Modbus protocol with separate ASCII/RTU and TCP ports for a variety of embedded systems. I can recommend FreeMODBUS based on first-hand experience replacing a DIY protocol stack in an embedded industrial controller with an 8-bit MPU. FreeMODBUS is licensed using the BSD 3-clause license.
libmodbus
libmodbus is a free open-source library for Linux, Mac OS X, FreeBSD, QNX and Win32. The library is written in C, supports RTU (serial) and TCP (Ethernet) communications, and is licensed using the BSD 3-clause license. QModMaster, pyModSlave and mbpoll (reviewed above) use libmodbus.
Other Resources
Peter Chipkin has a nice list of Modbus-related tools on the CHIPKIN website, including their own CAS Modbus Scanner, which is handy for investigating the functions, coils and registers supported by a device.
com0com is a free open-source kernel-mode virtual serial port driver for Windows. An unlimited number of virtual COM port pairs can be created, and any pair can be used to connect one COM port based application to another. The module is signed with a test certificate, and requires configuring Windows to load test-signed boot modules.
